Super glue and safety match
此文档为旧博客搬运。——2020.05.11
Super glue
-
The main ingredient in super glue is
Cyanoacrylate(氰基丙烯酸酯) which undergoes rapid anionic polymerization in the presence of water. The anionic here specifically means the hydroxide ions in the water. The hydroxide ion group plays as nucleophile and attacks the electron-poor alkene group to break the double bond. The ‘exposed’ carbon now is negatively charged and can likewise attack another cyanocrylate molecule. So by repeating this reaction, a polymer of cyanoacrylate can be formed to glue two faces together.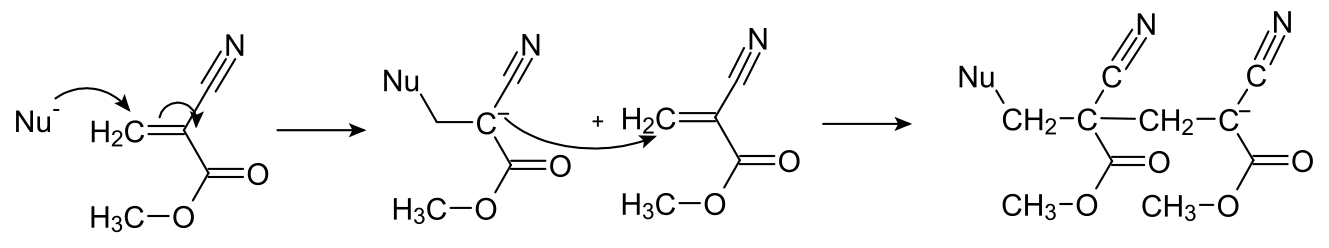
Read More:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyanoacrylate
- http://jwhitesell.ucsd.edu/documents/What_Makes_Superglue_so_Super.pdf
Safety match
- material coating the side of the match box: red phosphorus + glass fragments
- striking a match against the coating $\rightarrow$ heat created through friction $\rightarrow$ red phosphorus transformed into white phosphorus with the help of heat $\rightarrow$ white phosphorus reacts with the oxygen, releasing heat $\rightarrow$ potassium chlorate in the match head decomposed releasing oxygen, with the help of heat $\rightarrow$ burn, and burn steadily thanks to the reaction of Antimony trisulfide with oxygen (or potassium chlorate) , smelly due to the sulfur oxides produced $\rightarrow$ coating of paraffin wax ensures that the flame travels down the match in a controllable fashion.
- fire out, not too much smoke. This is because the match is soaked in ammonium phosphate, which smothers the residual heat and reduces the amount of smoke when the flame has been blown out.
Read More